[Spring] Throwable
Spring 예외처리
예외 처리의 목적은 서버에서 발생된 예외 상황이 최종 사용자에게 전달되는 것을 방지하기 위함이다. Spring 에서는 이를 위해 DAO 나 Service 에서 발생된 예외를 Controller 로 모아 처리하는 방법을 취한다.
조금 더 자세히 말하면 System 예외(Database SQL Error 등)가 발생하면 이를 Business 예외로 다시 던지는 re-throwing 방식을 사용한다. 이 때, @ExceptionHandler 와 @ControllerAdvice 를 사용하면 된다.
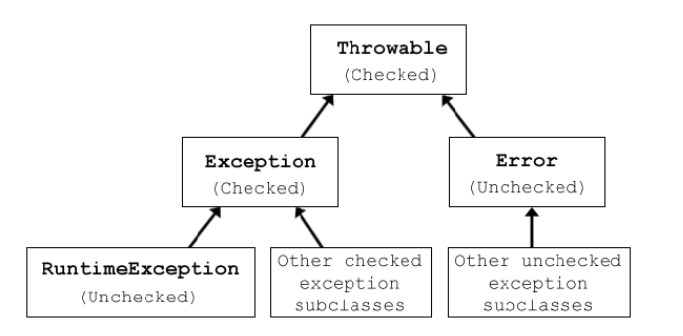
이렇게 예외를 re-throwing 할 때, 개발자가 한 가지 결정해줘야 할 것이 바로 Exception 을 상속받은 Checked Excpetion 을 만들 것인지, RuntimeException 을 상속받은 Unchecked Exception 으로 만들지이다.
논란의 여지가 있다고는 하는데.. RuntimeExeption 을 상속받은 Unchecked Exception 으로 만드는 것이 자동으로 앞단 Contoller 에 예외를 전달하기 수월해 이와 같은 방법을 채택한다고 한다.
※ Checked vs Unchecked 간단하게 말하면 명시적으로 try ~ catch 를 통해 잡아줘야하는 것을 Checked Exception, 런타임에 자동으로 잡아주는 것을 Unchecked Exception 이라 한다.
Spring 예외처리 특징
컨트롤러 기반
Layered Architecture 의 DAO 단이나 Service 단에서 발생한 예외가 Controller 로 전달되어 처리된다는 특징을 가진다. 이런 부가기능을 제공하는 Advice 클래스를 작성해야 하며, XML 설정 파일에 <aop:config>를 이용해 관점을 설정한다.
글로벌 Exception 핸들러
예외처리는 cross-cutting concern, 어플리케이션 전체에 포인트컷이 적용되어야 한다. 즉, 모든 과정에서 발생하는 예외를 처리한다는 뜻이다. @CongrollerAdvice 어노테이션을 포함한 클래스는 따라서 전역 예외처리 컨트롤러가 된다. 그리고 컨트롤러에서 캐치한 예외는 View 또는 JSON 응답으로 전해지게 된다.
@ControllerAdvice
스프링 3.2 이상에서 사용할 수 있는 어노테이션으로 @Controller나 @RestController 에서 발생하는 예외를 catch 한다. 스프링 4.0 이상에서는 특정 컨트롤러만 지정해 catch 하는 기능까지 사용할 수 있다.
해당 컨트롤러 어드바이스도 역시 빈이기 때문에 사용하기 위해서는 servelt-context.xml 에서 ControllerAdvice 를 include 해주어야 한다. 등록이 완료되면 @ControllerAdvice 로 빈(Bean)을 만들어주고, 내부에 @ExceptionHandler(Exception Type) 을 지정해 예외를 인자로 받는 메소드에 예외 타입을 적어주면, 발생한 에러에 따라 메서드를 동작시킬 수 있다.
Spring 4.0 이후부터는 @ControllerAdvice(annotation=RestController.class) 로 지정해주면 RestController 에만 대응되도록 만들 수 있다. 즉, 자동적으로 반환되는 방식이 JSON 형태가 된다.
MyBatis 예외처리
JDBC 관련 코드는 대부분 SQLException 이다. 이러한 SQLException 은 복구가 불가능한 예외이기 때문에 Spring-ByBatis 는 SQLException을 Unchecked 특징을 가진 RuntimeException 인 DataAccessException 으로 re-throwing 한다.
이렇게 전달된 DataAccessException 에서 SQLException 을 추출해 getErrorCode() 메서드를 사용해 에러코드를 확인하는 것이 가능하다.
예외처리 실습
먼저 BizException 이란 이름으로 사용자 정의 예외를 만든다. 이 때, Unchecked Exception 인 RuntimeException 을 상속한다. 그리고 Throwable 과 String msg 를 인자로 받는 생성자까지 세 가지를 아래와 같이 만들어 준다.
package com.example.hello.exception;
public class BizException extends RuntimeException{
public BizException() {
super();
}
public BizException(Throwable t) {
super(t);
}
public BizException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}
위 BizException 타입 에러를 처리할 ControllerAdvice 를 만들기 위해 아래와 같이 객체를 생성하고 내부에 핸들러에 클래스 타입을 지정해준다.
package com.example.hello.controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import com.example.hello.exception.BizException;
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(BizException.class)
public String handleBizException(Exception e, Model model) {
// error info
model.addAttribute("type", e.getClass().getSimpleName());
model.addAttribute("msg", e.getMessage());
// error.jsp 에 model 전달
return "error";
}
}
이후 Controller 에서 GET으로 접근되는 URL 중 한 곳에 testService() 메소드를 작성해준다.
@GetMapping("")
public String index() {
bbsService.testService();
return "index";
}
이 때, 주입된 bbsService 빈(Bean)은 다음과 같다. 중간에 throw new BizException("testService fail"); 을 통해 강제로 예외를 던지는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
package com.example.hello.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.example.hello.dao.ArticleDAO;
import com.example.hello.exception.BizException;
import com.example.hello.vo.Article;
@Service
public class BbsService {
@Autowired
private ArticleDAO articleDAO;
/* ... */
public void testService() {
System.out.println("executed");
throw new BizException("testService fail");
}
}
이제 서버를 실행해 Postman 으로 GET 요청을 전달하면 아래와 같이 예외가 정상적으로 발생해 jsp 파일로 전달되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
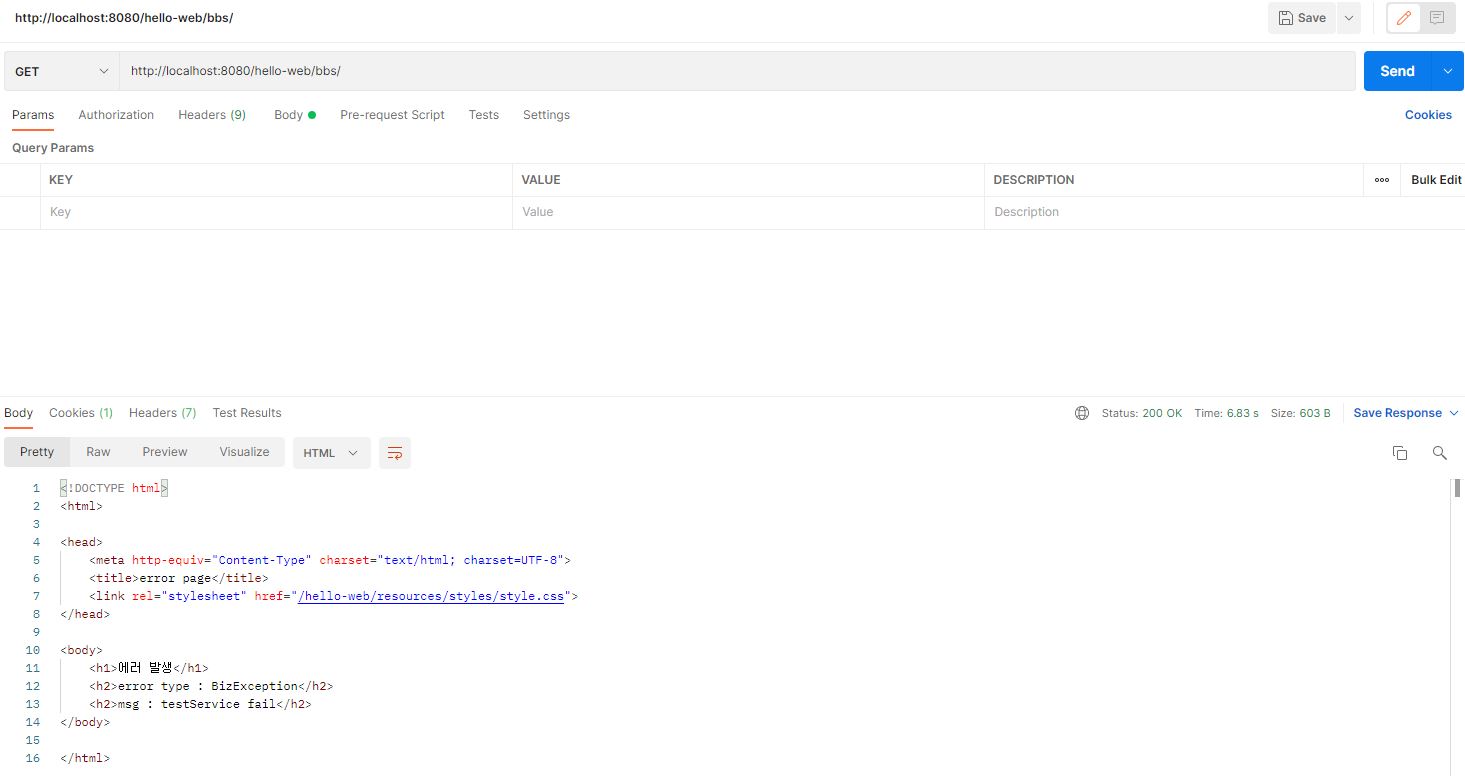
이와 비슷하게 @ExcptionHandler(MyBatisSystemException.class) 를 사용하면 Service 단에서 발생하는 SQLExcption 을 처리할 수 있다.

Leave a comment