[Matplotlib] Matplotlib 개요
Matplotlib 개요
Matplotlib 은 파이썬에서 데이터를 그래프나 차트로 시각화할 수 있는 라이브러리이다.
그래프 그려보기
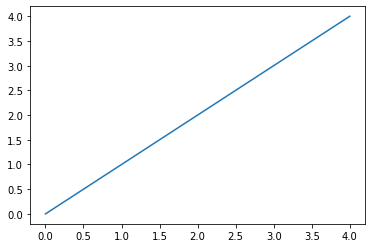
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.arange(5)
y = np.arange(5)
plt.plot(x, y)
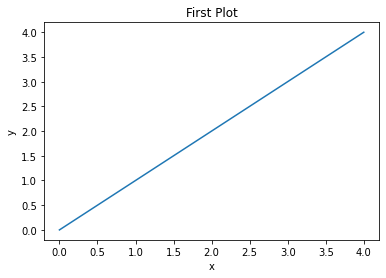
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.arange(5)
y = np.arange(5)
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.title("First Plot")
plt.xlabel("x")
plt.ylabel("y")
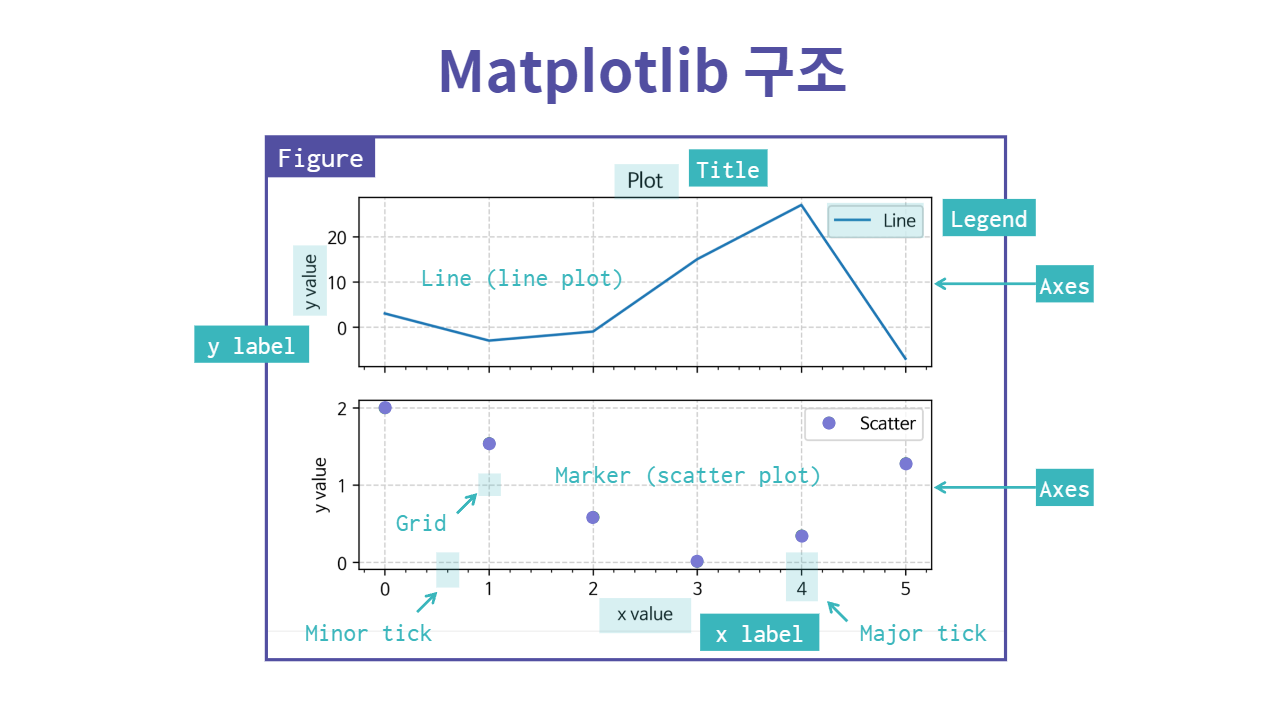
Matplotlib 구조
Matplotlib 구조는 아래와 같다.
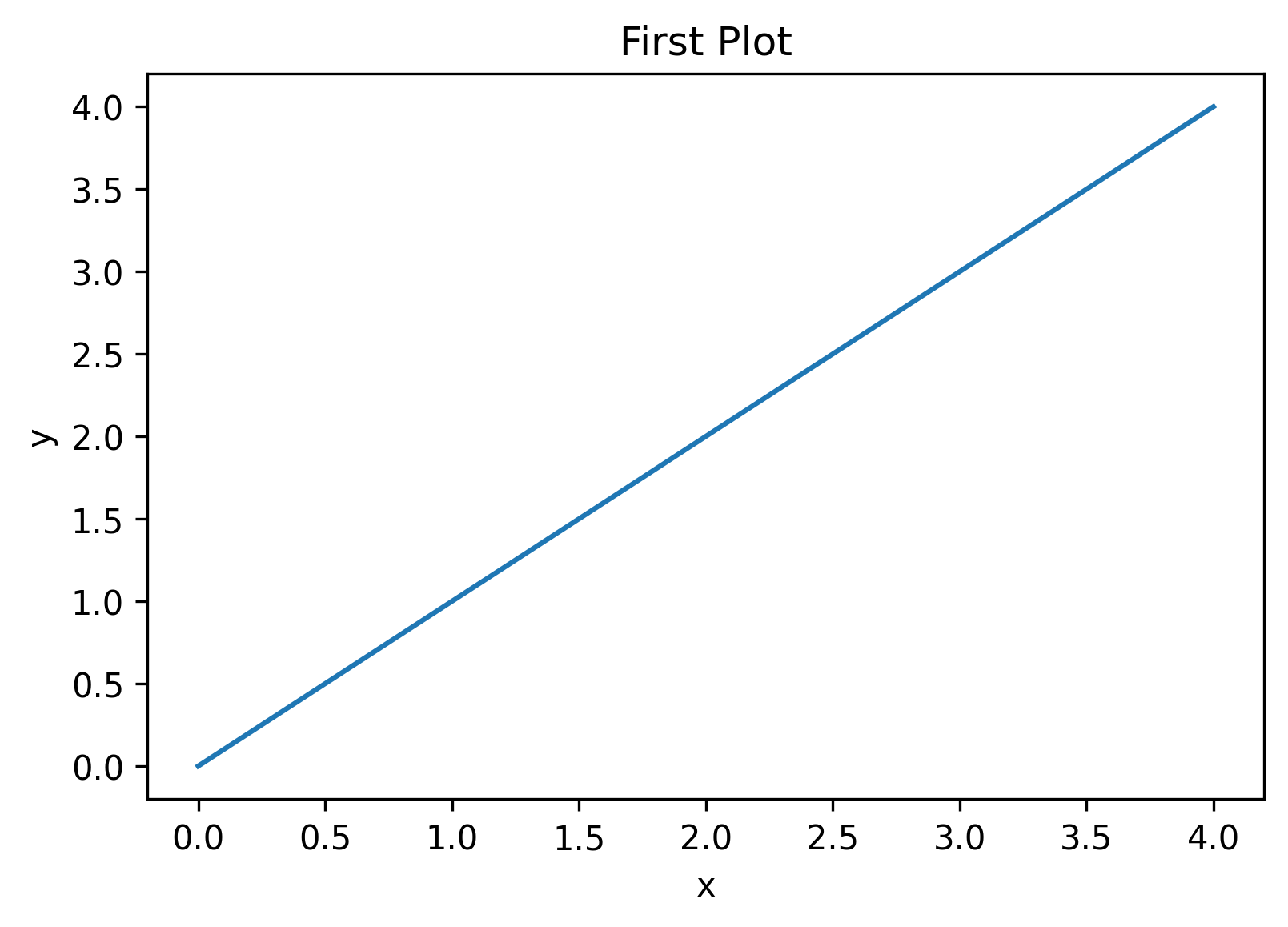
저장하기
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.arange(5)
y = np.arange(5)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(x, y)
ax.set_title("First Plot")
ax.set_xlabel("x")
ax.set_ylabel("y")
fig.set_dpi(300)
fig.savefig("/_img/2022-08-16/graph03.png")
그래프 여러 개 그리기
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.linspace(0, np.pi * 4, 100)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 1)
axes[0].plot(x, np.sin(x))
axes[0].set_xlabel("x")
axes[0].set_ylabel("sin(x)")
axes[1].plot(x, np.cos(x))
axes[1].set_xlabel("x")
axes[1].set_ylabel("cos(x)")
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.linspace(0, np.pi * 4, 100)
fig, axes = plt.subplots()
axes.plot(x, np.sin(x), label="sin(x)")
axes.plot(x, np.cos(x), label="cos(x)")
axes.set_xlabel("x")
axes.set_ylabel("y")
axes.legend(loc="upper right")
Line plot
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = np.arange(15)
y = x ** 2
ax.plot(
x, y,
linestyle=":",
marker="*",
color="blue"
)
Line style
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.arange(10)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(x, x, linestyle="-", label="solid")
ax.plot(x, x + 2, linestyle="--", label="dashed")
ax.plot(x, x + 4, linestyle="-.", label="dashdot")
ax.plot(x, x + 6, linestyle=":", label="dotted")
ax.legend(loc="lower right")
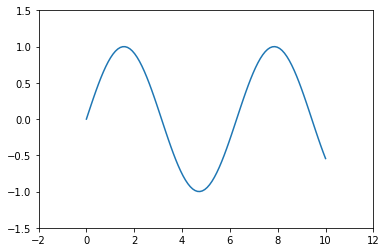
축 경계 조정하기
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(x, np.sin(x))
ax.set_xlim(-2, 12)
ax.set_ylim(-1.5, 1.5)
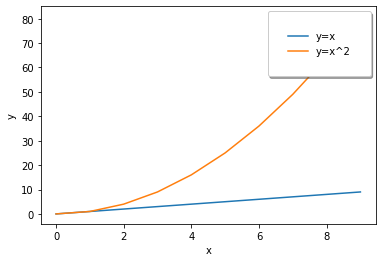
범례 (legend)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.arange(10)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(x, x, label='y=x')
ax.plot(x, x**2, label='y=x^2')
ax.set_xlabel("x")
ax.set_ylabel("y")
ax.legend(
loc='upper right',
shadow=True,
fancybox=True,
borderpad=2
)
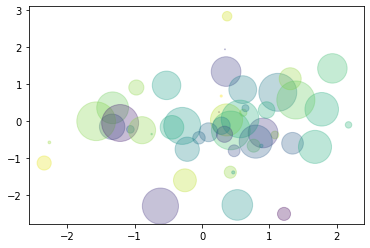
Scatter
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.random.randn(50)
y = np.random.randn(50)
colors = np.random.randint(0, 100, 50)
sizes = 500 * np.pi * np.random.rand(50) ** 2
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.scatter(
x, y,
c = colors,
s = sizes,
alpha = 0.3
)
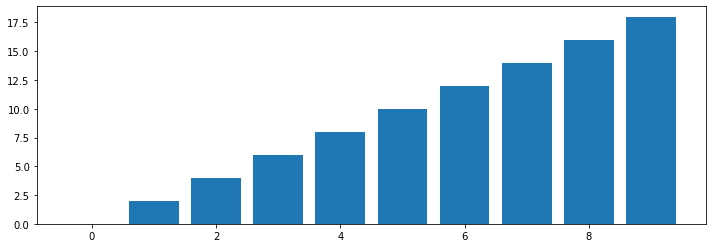
Bar
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.arange(10)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 4))
ax.bar(x, x*2)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.random.rand(3)
y = np.random.rand(3)
z = np.random.rand(3)
data = [x, y, z]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 4))
x_ax= np.arange(3)
for i in x_ax:
ax.bar(
x_ax,
data[i],
bottom=np.sum(data[:i], axis=0),
label = f"data[{i}]"
)
ax.set_xticks(x_ax)
ax.set_xticklabels(["A", "B", "C"])
ax.set_xlim(-1, 3)
ax.set_ylim(0, 3)
ax.legend(loc="upper right")
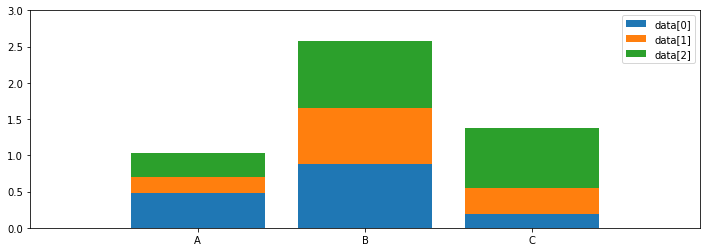
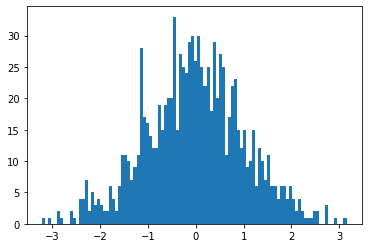
Histogram
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
data = np.random.randn(1000)
ax.hist(data, bins=100)

Leave a comment