[Design Pattern] Strategy Pattern (전략 패턴)
Strategy Pattern
전략 패턴은 캡슐화된 특정한 알고리즘의 변화를 유연하게 만들어주는 디자인 패턴이다. 일반적으로 전략 패턴은 특정한 클래스들의 차이가 특정한 행동이거나 동일한 대상에 다양한 버전의 알고리즘을 적용해야 하는 경우 사용된다.
- Purpose
- Defines a set of encapsulated algorithms that can be swapped to carry out a specific behavior
- Use When
- The only diffenece between many related classes is their behavior
- Multiple versions or variations of an algorithm are required
- The behavior of a class should be defined at runtime
- Conditional statements are complex and hard to maintain
아래와 같은 클래스 다이어그램이 있다고 가정하자. 클래스 다이어그램은 요구사항에 따라 모든 오리는 quack()을 통해 울고, 같은 방법으로 수영하고, 종류마다 자신을 뽐내는 방법을 가지도록 구성되었다.
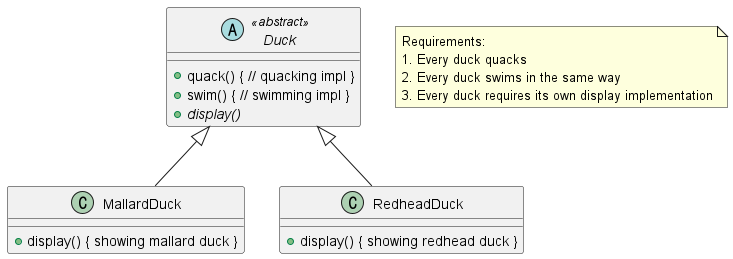
그런데 여기서 한 가지 요구사항이 추가되었다. 바로 오리가 날 수 있다는 사실을 고려하지 않은 것이다. 오리가 날 수 있다는 내용을 추가해 수정한 뒤 아래와 같이 고무 오리 클래스를 만들었다
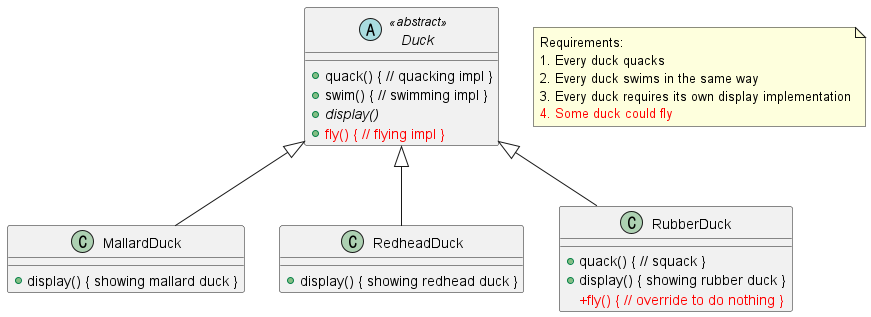
고무 오리는 날 수 없기 때문에 아무 것도 하지 않도록 Override하며 다른 오리들과는 다른 소리를 내기 때문에 quack() 구현부 역시 달라지게 된다. 이와 같은 경우는 계속해서 발생 가능한데, 만약 DecoyDuck이라는 미끼용 오리가 추가되면 quack()을 Override하고 fly()를 선언해 아무 것도 구현하지 않는 클래스가 하나 더 생길 수 있다. 불필요한 기능들을 포함하게 되어 SRP를 어기는 것으로 여길 수 있다.
이와 같은 상황에서 아래와 같은 방식으로 설계를 수행해 볼 수 있다. 그러나 아래 구성도 완벽한 설계가 되지 못 한다. 먼저 Code reuse 측면에서 같은 fly() 동작이어도 중복된 작성이 필요하며 공통 동작을 수정하는데에도 많은 시간이 투자된다.
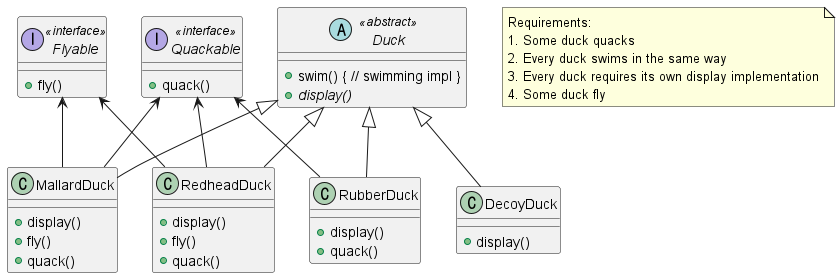
이를 해결하기 위해 Program to an interface, not an implementation 원칙을 적용해 아래와 같은 행위를 정의한다. 이렇게 행위가 적용되면 클라이언트는 단순히 FlyBehavior Reference Type을 가지고 여러 행위들을 사용 할 수 있게 된다.
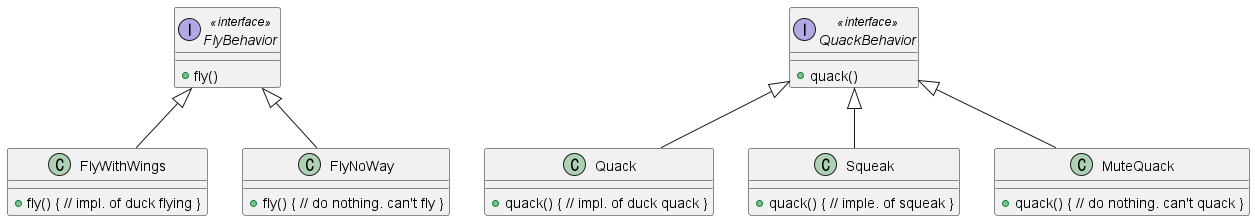
해당 설계를 고려한 Duck Class는 아래와 같이 나타낼 수 있으며, 해당 클래스에 Object Composition과 Delegation(위임)을 확인할 수 있다. 그리고 결론적으로 아래 예시처럼 클래스들은 반드시 Polymorphic Behavior와 Code Reuse를 달성해야 한다.
이와 같은 이유로 상속(Inheritance)보다는 포함(Composition)을 추구하는 것을 권장한다. Composition 관계에서는 나아가 권한의 위임 역시 가능해 Change Propagation으로부터 보다 유연하고 자유로운 설계를 만들 수 있다. 이를 Design Principle: Favor composition over inheritance 이라 표현 할 수 있다.
public abstract class Duck {
FlyBehavior flyBehavior; // Object Composition
QuackBehavior quackBehavior; // Object Composition
public Duck() {}
public abstract void display();
public void performFly(){ // Delegation
flyBehavior.fly();
}
public void performQuack(){ // Delegation
quackBehavior.quack();
}
public void swim(){
System.out.println("All ducks float!");
}
public void setFlyBehavior(FlyBehavior fb){
flyBehavior = fb;
}
public void setQuackBehavior(QuackBehavior qb){
quackBehavior = qb;
}
}
끝으로 재사용의 입장에서 Class Inheritance와 Object Composition을 간단하게 비교해 정리했다. 이는 LSP를 위반하는 Queue 클래스를 Composition으로 해결하는 예제를 떠올리며 읽으면 더 쉽게 이해 할 수 있다.
- Class Inheritance
- subclass’s implementation is defined in terms of the parent class’s implementation
- the parent class implementation is often visible to the subclasses
- it’s called as White-box reuse
- pros
- done at compile-time
- easy to use
- cons
- the subclass becomes dependent on the parent class implementation
- the inheried implementation cannot be changed at run-time
- Object Composition
- objects are composed to achive more complex funcionality
- needs well-defined interfaces since the internals of the objects are unknown
- funcionality is acquired dynamically at run-time by utilizing references to other objects
- it’s called as Black-box reuse
- pros
- implementation can be replaced at run-time
- less implementation dependencies
- cons
- harder to understand
Structure of strategy pattern
- Strategy Pattern
- Defines a family of algorithms
- Encapsulates each one and makes them inerchangeable
- Strategy Pattern lets the algorithm vary independently from clients that use it
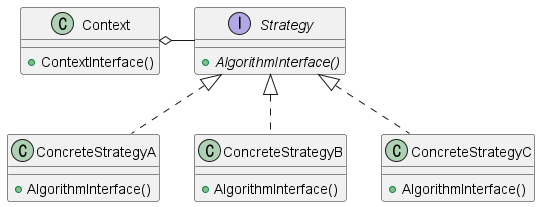
이러한 전략 패턴이 적용된 간단한 예로 Sorting Example을 들 수 있다. 배열을 정렬하는 방법은 quick sort, merge sort, buble sort 등으로 다양하다. 배열 클래스는 정렬 알고리즘 인터페이스를 가지고 있고, 실제 구현 클래스는 Composition 하고 있는 경우를 위 구조에 맞춰 생각해 볼 수 있다.
Keep in mind
- Knowing the OO basics does not make you a good OO designer
- Good OO design are reusable, extensible and maintainable
- Patterns don’t give you code, they give you general solutions to design problems
- Most patterns and principles address issues of change in software

Leave a comment