[Design Pattern] Observer Pattern (관찰자 패턴)
Observer Pattern
Observer Pattern은 Publish/Subscribe model로도 불리는 패턴으로, 이 관찰자 패턴은 한 개 또는 여러 객체들의 상태 변화를 감지해 다른 객체들에게 전달하기 위해 사용된다. 아래는 짤막한 정리와 관찰자 패턴을 정의한 내용을 정의했다.
- Purpose
- Lets one or more objects be notified of state changes in other objects within the system
- Use When
- Loose coupling is needed for communications
- State changes in one or more objects should trigger behavior in other objects
- Broadcasting capabilities are required
- An understanding exists that objects will be blind to the expense of notification
※ The Observer Pattern Defined
The Observer Pattern defines a one-to-many dependency between objects so that when one object change state, all of its dependents are notified and updated automatically
Weather Problem
관찰자 패턴을 적용해보기 위한 문제 상황을 아래 그림과 같이 가정해보자. 세 개의 센서로부터 측정되는 값을 표시하기 위해 Weather Station과 WeatherData Object가 있다고 가정해보자. WeatherData Object 의 클래스 다이어그램은 우측 상단에 표시되어 있으며 각 세 개의 메소드는 가장 최근 측정된 날씨 정보를 반환한다.
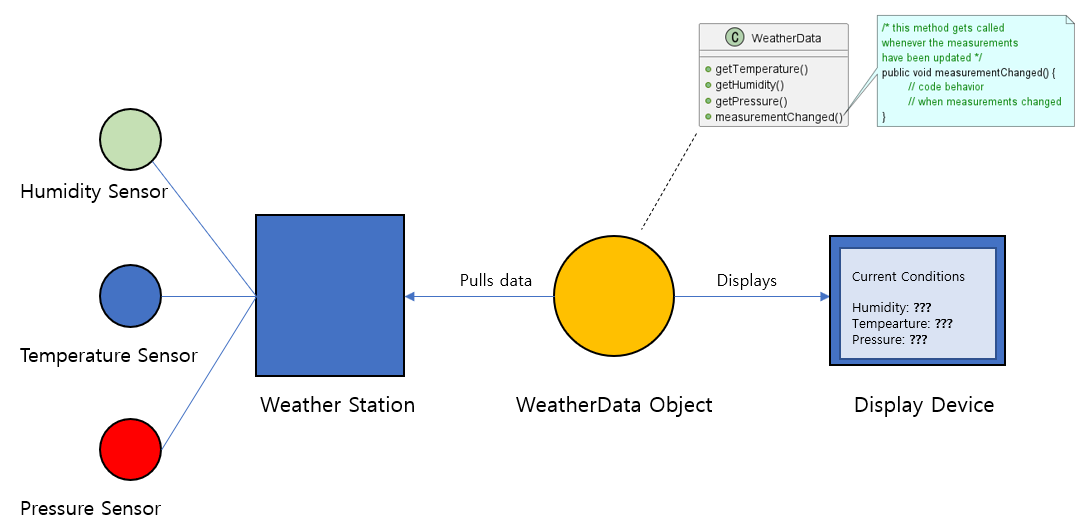
WeatherData는 세 개의 센서를 가지고 있고, 이들 값이 전달되어 변화를 감지하면 Display Device는 이를 알아차리고 Display Device가 가진 각 모드들에게 정보를 전달하는 것이 요구사항이라고 생각해보자. 만약 WeatherData를 이용하는 Display Device 모드가 current condition, statics, forecast 세 가지가 있을 때, 간단하게 WeatherData를 구현할 수 있다.
public class WeatherData{
// variables
public void measurementsChagned(){
float temp = getTemperature();
float humidity = getHumidity();
float pressure = getPressure();
currentConditionDisplay.update(temp, humidity, pressure);
statisticsDisplay.update(temp, humidity, pressure);
forecastDisplay.update(temp, humidity, pressure);
}
// other weatherData methods here
}
void measurementsChanged() 메소드 안에서 각 디바이스 모드 정보를 변경해주는 작업을 수행하고 있다. 그러나 이 부분은 코드는 디바이스 모드가 추가되거나 매개변수 종류가 변할 때마다 함께 수정되어야 하는 번거로움을 가진다. 이렇게 변화를 감지하고 변경된 값을 전달하는 효율적인 구조로 Observer Pattern을 사용할 수 있다.
Compare to Publishser/Subscriber Model
앞서 Observer Pattern이 어떤 상황에서 사용되는지를 확인했다. 이와 같은 Observer Pattern을 Publisher/Subscriber Model과 비교하면 Publisher:Subscriber = Subject:Observer로 나타낼 수 있다. Observer들은 Subject를 구독하거나 구독을 끊을 수 있으며, 해당 Subject의 변경이 일어나면 Subject는 변경된 정보를 전달해준다.
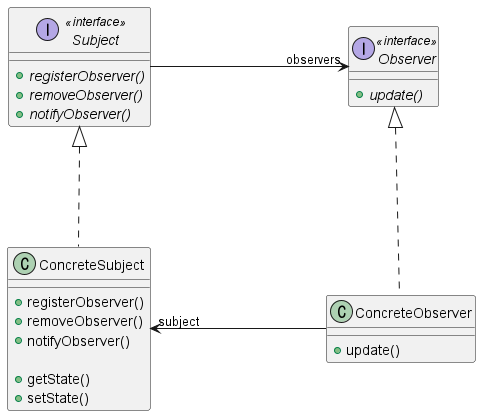
Sturcture of observer pattern
관찰자 패턴 클래스 다이어그램은 아래와 같다. 여기서 중요한 것은 ConcreteSubject는 ConcreteObserver 정보를 모른다는 것이다. 가지고 있는 정보는 오직 Observer Interface 뿐이기 때문에 다양한 ConcreteObserver들을 사용 할 수 있다. 이러한 패턴은 Model은 View 정보를 철저히 모른 상태로 데이터를 전달해야하는 MVC 패턴에서도 사용된다.
이러한 패턴 구조를 앞선 문제에 적용해보면 아래와 같이 나타낼 수 있다. Observer들은 WeatherData::registerObserver() 를 통해 등록되어 notifyObserver()를 통해 각각의 update()를 호출 할 수 있게 한다.
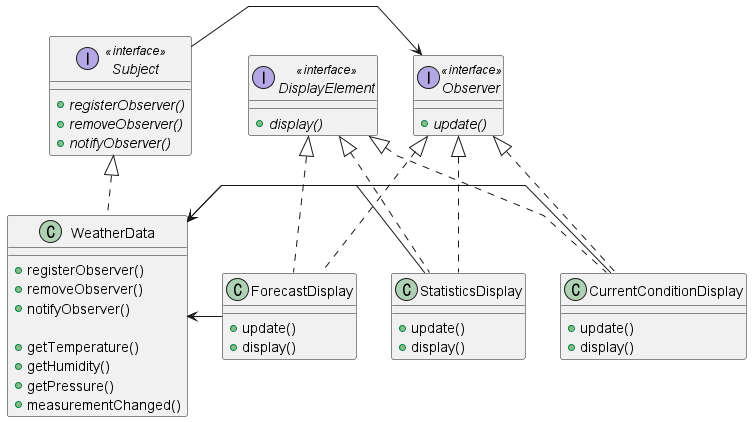
The Power of Loose Coupling
- Principle of loose coupling
- Strive for loosely coupled designs between object that interact
- When two objects are loosely coupled, they can interact, but have little knowledge of each other
- Observer Pattern provides an object design where subjects and observers are loosely coupled
Observer pattern in Java
Java에는 Observer Interface를 지원한다. Observable을 상속해 사용하면 이를 앞서 구현했던 등록, 삭제, 알림 등을 구현하지 않고 사용할 수 있다.
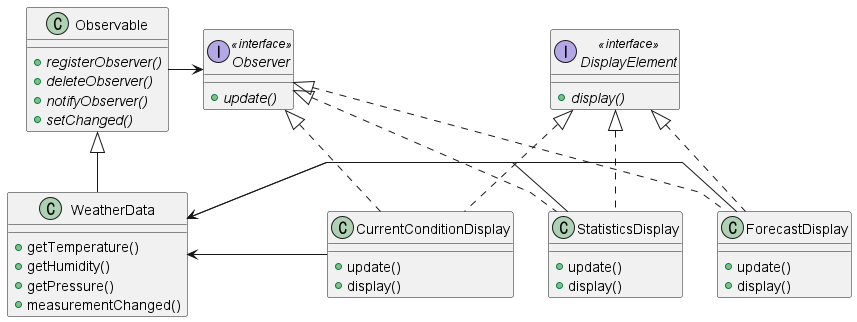
- Observable (Publisher) side
- To send notification
- Call setChanged()
- Call either notifyObserver() or notifyObserver(Object arg)
- To send notification
- Observer (Subscriber) side
- To become an observer
- Implement java.util.Observer interface
- To subscribe
- Call addObserver() on any Observable object
- To unsubscribe
- Call deleteObserver()
- To get updated
- Implement update(Observable obs, Object arg)
- To become an observer
setChanged()
setChanged() {
changed = true;
}
notifyObserver(Object arg){
if(changed){
for every observer on the list {
call update(this, arg)
}
changed = false;
}
}
notifyObservers() {
notifyObservers(null);
}
- setChanged() method is there to give you more flexibility
- Optimize the notifications
- Example:
- If the sensor reading is very sensitive, you may not want to update
- setChanged() allows you to control the notification points
- Other relevant methods in Observable
- clearChanged()
- hasChanged()
Stock price subscribing example
Observer Pattern은 앞서 말했던 것처럼 주로 이벤트 처리와 GUI 프로그래밍에서 사용되나 활용하는 사람에 따라 다양한 상황에 역시 적용할 수 있다. 핵심은 Observer 목록을 만들고, 상태 변화가 있을 때 Subject에서 등록된 모든 Observer에 정보를 전달하는 것이다.
-
Subject: 상태 변화를 감시하는 대상 객체 또는 인터페이스. addObserver()와 removeObserver() 메서드를 통해 옵저버를 등록하고 제거할 수 있으며, notifyObservers() 메서드를 통해 옵저버들에게 상태 변화를 알린다.
-
Observer: Subject의 상태 변화를 관찰하는 객체 또는 인터페이스. update() 메서드를 통해 상태 변화가 있을 때마다 수행해야 하는 작업을 정의한다.
-
ConcreteSubject: Subject 클래스의 구현체. 상태를 가지고 있으며, 상태가 변화될 때마다 등록된 옵저버들에게 알린다.
-
ConcreteObserver: Observer 클래스의 구현체. Subject 클래스로부터 알림을 받아 update() 메서드를 수행한다.
아래는 간단한 예시로 주식 가격 변동을 감시하는 주식 거래소 프로그램이다. 먼저 감시 대상인 StockMarket 클래스는 Subject 인터페이스를 구현한다. addObserver, removeObserver, notifyObservers 메서드를 구현하여 Observer 인터페이스를 구현한 객체들을 등록, 삭제하고, 변화를 감지해 옵저버들에게 알린다.
class StockMarket implements Subject {
private List<Observer> observers;
private double price;
public StockMarket() {
observers = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void addObserver(Observer observer) {
observers.add(observer);
}
public void removeObserver(Observer observer) {
observers.remove(observer);
}
public void notifyObservers() {
for (Observer observer : observers) {
observer.update(price);
}
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
notifyObservers();
}
}
Investor 클래스는 Observer 인터페이스를 구현하고, update 메서드를 구현하여 변화가 있을 때마다 어떤 작업을 수행할 것인지 정의한다. 이로써 데이터 처리와 변화 감지라는 두 가지 Concern을 분리할 수 있다.
class Investor implements Observer {
private String name;
public Investor(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void update(double price) {
System.out.println(name + " received a notification: The stock price is now " + price);
}
}
끝으로, 주식 거래소 프로그램을 실행하기 위해서는 StockMarket 객체와 Investor 객체를 생성하고, StockMarket 객체에 Investor 객체를 등록해야 한다. 그리고 setPrice 메서드를 호출하여 주식 가격이 변동되면 notifyObservers 메서드가 호출되어 등록된 Investor 객체들에게 변경된 데이터를 알린다.
아래 예제에서는 John과 Jane이라는 두 명의 투자자를 Investor 객체로 생성하고, addObserver 메서드를 호출하여 StockMarket 객체에 등록하고 있다. 그리고 setPrice 메서드를 호출하여 주식 가격이 변동되면, StockMarket 객체의 notifyObservers 메서드가 호출되어 Investor 객체들의 update 메서드가 실행되는 것을 확인할 수 있다. 마지막으로 removeObserver 메서드를 호출하여 Jane 투자자를 제거하고, 다시 setPrice 메서드를 호출하여 John 투자자에게만 주식 가격 변동을 알리도록 설정하는 것으로 테스트가 마무리 된다.
public static void main(String[] args) {
StockMarket stockMarket = new StockMarket();
Investor investor1 = new Investor("John");
Investor investor2 = new Investor("Jane");
stockMarket.addObserver(investor1);
stockMarket.addObserver(investor2);
stockMarket.setPrice(100.00);
stockMarket.setPrice(150.00);
stockMarket.removeObserver(investor2);
stockMarket.setPrice(200.00);
}

Leave a comment