[Design Pattern] Object-Oriented Paradigm
Object-Oriented Paradigm
Abstrct Data Type (ADT)
추상 자료형으로 번역되는 ADT는 자료들과 그 자료들에 대한 연산들을 명기한 것으로 인터페이스와 구현을 분리해 추상화 계층을 둔 것이라 설명한다. 이런 ADT에 대한 설명을 읽다보면 자료 구조와의 차이점이 무엇인지 궁금해질 수 있다. 이 질문에 답하기 위해 What is the difference between an Abstract Data Type(ADT) and a Data Structure? [closed] 라는 Stack Overflow 답변을 가져왔다.
To put it simple, ADT is a logical description and data structure is concrete. ADT is the logical picture of the data and the operations to manipulate the component elements of the data. Data structure is the actual representation of the data during the implementation and the algorithms to manipulate the data elements. ADT is in the logical level and data structure is in the implementation level.
추상 자료형은 데이터나 정보를 논리적인 형태로 나타낸 것이고 자료구조는 추상적인 개념을 실질적으로 구현한 것이라 설명한다. 즉, ADT는 하나의 논리적으로 표현된 개념으로 이해하고 있다.
그리고 이러한 ADT는 Single syntactic unit로 구현된다고 하는데, 컴퓨터 공학부 과정에서 언어를 만드는 과제를 진행 할 때 배우는 개념이라고 들었다. 이 부분은 자세히 알지 못 해 설명을 남겨두며 추후 정리해보려고 한다.
Object-Oriented Paradigm
객체지향 패러다임을 적용하면 클라이언트 코드 레벨에서도 이득을 얻을 수 있다. 예를 들어, Polymorphism을 통해 Conditional Statement를 추가하지 않고서도 변형을 적용 할 수 있다. 또한, 기존에 작성한 코드를 상속받아 재사용 할 수 있어 클라언트 코드에 중복된 코드를 작성하지 않아도 된다.
Class = ADT + Inheritance + Polymorphism
Inheritance
클래스 B가 클래스 A를 상속할 때, 먼저 B는 A의 모든 메소드를 상속한다. 그렇기 때문에 A에게 전달되는 모든 메시지를 B도 처리 가능하다. 또한, B는 A의 모든 메소드를 상속하기 때문에 is a 관계가 성립된다. 그렇기 때문에 클래스 B의 모든 인스턴스들은 A의 인스턴스라고 여길 수 있다. 결론적으로 클래스 A가 사용되는 모든 곳에는 클래스 B가 사용될 수 있다.
Polymorphism
Polymorphism을 사용하는 변수라는 뜻의 Polymorphic variable은 자식 관계 또는 실체화 관계에 있는 특정한 인스턴스를 Reference 할 수 있는 클래스로 정의된다.
A polymorphic variable can be defined in a class that is able to reference objects of the class and objects of any of its descendants.
만약 Polymorphic Variable인 클래스가 오버라이드 된 메소드를 가지고 있는 상태에서 해당 메소드가 호출되었다면, 동적으로 정확한 메소드에 바인딩되어 동작한다. 이러한 성질을 이용하면 개발과 유지 관점에서 소프트웨어 시스템을 쉽게 확장시킬 수 있다.
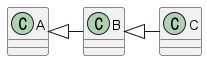
예를 들어 C는 B를 상속하고, B는 A를 상속하는 관계가 있다고 가정해보자. 그렇다면 A를 통해서 B 또는 C에 오버라이드된 메소드를 사용 할 수 있다. 여기서 중요한 것은 앞서 말했던 하위 관계에서 역으로 상위 클래스를 참조하는 것은 불가함을 명심해야 한다.
A a = new B(); // Possible
A a = new C(); // Possible
B b = new C(); // Possible
C c = new A(); // Impossible
C c = new B(); // Impossible
B b = new A(); // Impossible
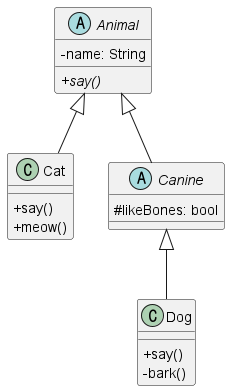
예제 문제를 통해 이해가 제대로 되었는지 확인해보자. 아래와 같은 관계의 클래스 다이어그램을 보고 작성된 코드 중 컴파일 에러가 발생하는 부분을 찾아보자. 먼저 PlantUML에서 해당 클래스 다이어그램을 그리는 코드를 첨부한다.
@startuml
skinparam classAttributeIconSize 0
abstract class Animal {
-name: String
+{abstract}say()
}
class Cat {
+say()
+meow()
}
abstract class Canine {
#likeBones: bool
}
class Dog {
+say()
-bark()
}
Animal <|-- Cat
Animal <|-- Canine
Canine <|-- Dog
@enduml
Animal a = null;
Dog dog0 = new Dog();
Cat cat0 = new Cat();
a = dog0;
a.say();
a = cat0;
a.say();
Animal cat1 = new Animal(); // Error: Abstract class can't use new
Animal cat2 = new Cat();
Cat cat3 = new Animal(); // Error: Abstract class can't use new
Cat cat4 = new Cat();
Animal dog1 = new Canine(); // Error: Abstract class can't use new
Animal dog2 = new Dog();
Canine dog3 = new Dog();
Canine dog4 = new Cat(); // Error: Siblings can't be refereneced
Dog dog5 = new Canine(); // Error: Abstract class can't use new
Dog dog6 = new Dog();
끝으로 상속이나 실체화를 통해 형성된 클래스 다이어그램에서 어떤 메소드가 실행되는지를 찾는 규칙을 설명하기 위해 How a decision is made about which method to run 으로 설명된 자료를 첨부했다.
- Step 1: If there is a concrete method for the operation in the current class, run that method.
- Step 2: Otherwise, check in the immediate superclass to see if there is method there; if so, run it.
- Step 3: Repeat step 2, looking in successively higher superclasses until a concrete method is found and run.
- Step 4: If no method si found, then there must be an error. In compile time, it shows an error message.
What is an Interface?
Interface는 Abstract Class보다 더욱 추상화된 것으로 extends 키워드를 통해 상속을 수행하는 추상 클래스와 달리 implements 키워드를 사용해 클래스를 사용한다. 이러한 인터페이스는 static 변수를 제외하고는 그 어떤 변수나 실질 메소드를 포함하지 않는다.
만약 아무런 제약 사항이 없다면 Abstract Class보다 Interface를 사용하는 것이 권장된다. 클래스와는 달리 인터페이스는 다중 구현이 가능하며 더욱 추상화된 구조를 가지고 있어 약한 결합을 제공하기 때문이다.
Polymorphism Examples with Interface
Abstract class를 extends하는 경우와 마찬가지로 Interface를 implements하는 경우에도 다형성을 적용할 수 있다. ISayable라는 이름의 인터페이스가 있을 때, 좌변에는 Interface Reference를 선언할 수 있다. 가령 ISayable을 구현하는 Person 클래스는 다음과 같이 선언할 수 있다. 그러나 Interface는 Abstract class와 마찬가지로 인스턴스화 될 수 없기 때문에 우변에서 생성자와 함께 사용되는 것은 불가능하다.
ISayable ifRef = new Person(); // Possible
Person personRef = new ISayable // Impossible
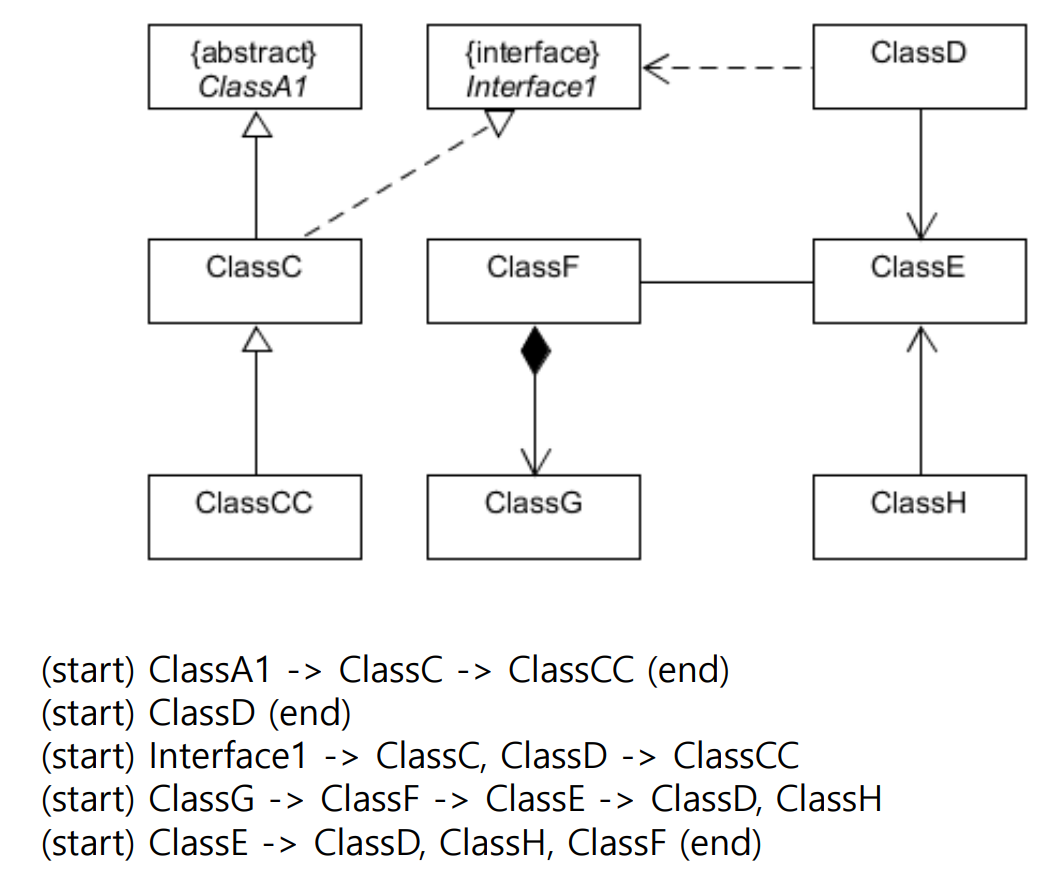
Class Relationships and Change Propagations
Source의 변화에도 Target은 변화하지 않는다. 아래 그림은 변화에 따라 어디까지 그 영향이 미치는지를 표현한 그림이다. Relationship에서 화살표 유무에 따라 Propagation이 달라질 수 있음을 주의하자.

Leave a comment