[Design Pattern] GRASP Principle
GRASP Principle
GRASP은 General Responsibility Assignment Software Patterns의 약자로 Craig Larman의 9가지 설계 원칙으로 설명된다. OOAD에서는 요구사항을 분석하고 도메인 모델을 만든 뒤 최종 소프트웨어를 설계한다. 이 때, GRASP은 객체 지향 소프트웨어 설계 과정에서 어떤 클래스가 Responsibility를 가져야 하는지와 Object Collaboration을 결정하는 부분에 도움을 준다.
이러한 GRASP의 9가지 Principle은 아래와 같다.
- Information Expert
- Creator
- Controller
- Low Coupling
- High Cohension
- Polymorphism
- Pure Fabrication
- Indirection
- Protected Variation
Modularity
모듈성(Modularity)는 소프트웨어가 얼마나 잘 모듈화되어 있는가를 말한다. 좋은 설계는 시스템을 모듈 단위로 나누어 각 모듈에 적절한 책임을 부과한다. 이러한 모듈성은 프로그래머가 문제를 풀기 위해 다뤄야하는 영역이나 복잡도를 감소시켜준다.
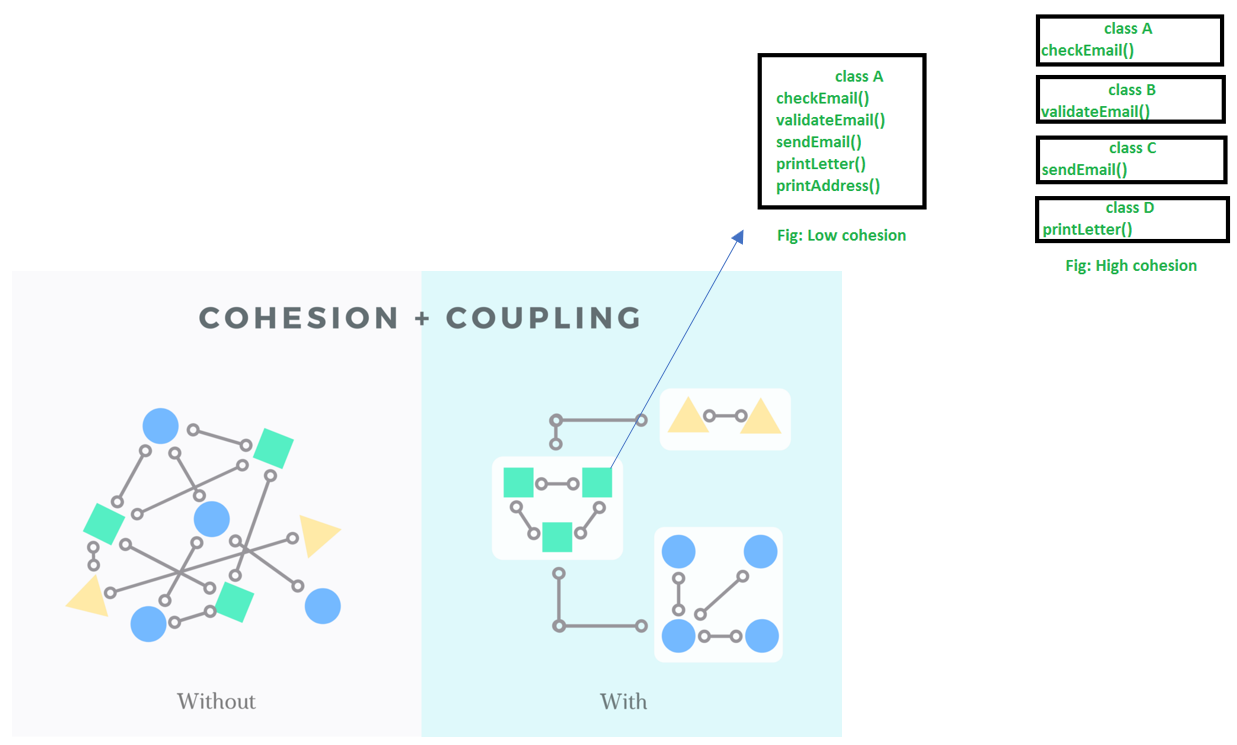
모듈화가 잘 되어있다는 것은 모듈이 가진 함수가 특정 문제 영역과 관련있는 부분들끼리 묶여있으며, 잘 정의된 간결한 인터페이스들로 연결되어 있다는 것을 뜻한다. 이러한 성질을 측정하는데 사용되는 개념이 Coupling과 Cohesion인데, 그 개념은 아래와 같다. 커플링은 낮고, 응집도는 높아야 모듈화가 잘 되어있다고 할 수 있다.
- Coupling: measure of the inter-dependencies between modules
- Cohesion: measure of how strongly the elements in a module are related
Coupling을 설명하는 방법은 다양하며, 일반적으로 attribute referencing, method referencing, subclass, implements 등을 모두 커플링이라고 할 수 있다. 이와 같은 커플링이 많아져 높은 커플링이 생기면 의존하고있는 클래스들까지도 변경을 강제하며 재사용과 고립을 어렵게 만든다.
Cohesion은 비슷한 유형의 메소드를 수행하는 모듈이 얼마나 많이 모여있는가를 뜻한다. 예를 들어 메소드 4개를 한 개의 클래스에 넣어 놓으면 모듈 단위는 1개가 되지만, 이 메소드 4개를 각각의 클래스로 나누어 관리하면 모듈 단위는 4개가 될 수 있다.
결론적으로 앞서 설명한 Cohesion과 Coupling을 모식화한 그림이 아래와 같다. 다양한 커플링을 지우고 한 곳으로 응집도를 모아 간결한 구조를 만들고 있다.
Creator Pattern
- Name: Creator
- Problem: Who creates an A?
- Solution: Assign class B the responsibility to create an instance of class A, if one of these is true (the more th better):
- B contains or aggregates A
- B records A
- B closely uses A
- B has the initializing data for A
- if there is a choice, prefer “B contains or aggregates A”
- Discussion:
- Guides assigning creation responsibilities
- Contraindication: creation may require significant complexity
- using recycled instances for performance reasons
- conditionally creating an instace from one of a family of similar classes
- sometimes desired to outsource object wiring(dependency injection)
- Benefits:
- Low Coupling is supported
- Related patterns:
- Abstract Factory, Singleton
Information Expert Pattern
- Name: Information Expert
- Problem: What is a basic principle by which to assign responsibilities to object?
- Solution: Assign a responsibility to the class that has the information needed to fulfill it.
- Discussion
- Most used principle in the assignment of responsibilities
- Information spread across different objects may makes objects need to interact
- Contraindication: Conflict with Seperation of Concerns
- Example: Responsibility for saving a sale information in the database
- Adding this responsibiliy to Sale distribute database logic over many classes, then cause low cohesion
- Benefits
- Information encapsulation supports low coupling
Controller Pattern
- Name: Controller
- Problem: What first object beyond the UI layer receives and coordinate or controls a system operation?
- Assgin the responsibility o an object representing one of these choices:
- first option: Overall system, a root object, a device that the software is running within, or a major subsystem (facade controller)
- second option: Use case scenario within which the system operation occurs (Use case or session controller)
- Discussion
- Controller class is called bloated if overloaded with too many responsibilities
- Add more controllers(facade → use-case controllers)
- Delegates to other objects
- Controller class is called bloated if overloaded with too many responsibilities
- Benefits
- No application logic in the GUI makes increased potential for reusable components
- Use case controller is useful when operation must be performed in a specific order
Low Coupling Pattern
- Name: Low Coupling
- Problem: How to reduce the impact of change?
- Solution
- Assign responsibilities so that unnecessary coupling remains low.
- Use this principle to evaluate alternatives
- Discussion
- Low coupling encourages designs to be more independent which reduces the impact of change.
- Needs to be considered with other patterns such as Information Expert and High Cohesion.
- High coupling to stable global objects is not problematic (ex: coupling to Java libraries such as java.util)
High Cohesion Pattern
- Name: High Cohesion
- Problem: How to keep objects focused, understandable, and manageable, and as a side effect, support Low Coupling?
- Solution
- Assgin responsibilities so that cohesion remain high.
- Use this to evaluate alternatives.
Pure Fabrication Pattern
- Name: Pure Fabrication
- Problem: Who is responsible when you are desperate, and do not want to vialte high cohesion and low coupling?
- Solution:
- Assign a highly cohesive set of responsibilities to an artificial or convenience “behavior” class that does not represent a problem domain concept
- Something made up, in order to support high cohesion, low coupling, and reuse.
- For example, create a new class that is solely responsible for saving objects in a persistent storage medium by Pure Fabrication
Polymorphism Pattern
- Name: Polymorphism
- Problem: Whe is responsible when behavior varies by type?
- Solution
- When related alternatives or behaviors vary by type(class), assign reseponsibility for the behavior using polymorphic operations to the types for which the behavior varies.
- Discussion
- fundamental principle in design: how to handle similar variations
- Avoid excessive use for “future-proofing” against yet unknown potential future variations
- Add the variation point only when the need arises (to detect timing, use TDD)
- Benefits
- Easier and more reliable than using explicit selection logic
- Easier to add additional behaviors later on
- Costs
- Increases the number classes in a design
- May make the code less easy to follow
Indirection Pattern
- Name: Indirection
- Problem: How to assign responsiblities o avoid direct coupling?
- Solution
- Assign the responsibility to an intermediate object to mediate between other components or services, so that they are not directly coupled.
- Indirection introduces an intermediate units (classes) o communicate between the other units, so that the other units are not directly coupled.
- Benefits
- Low Coupling
- Example: Adapter, Facade, Proxy, Mediator, …
Protected Variations Pattern
- Name: Protected Variations
- Problem: How to assign respsonsibilities to objects, subsystems, and systems so that the variations or instability in these elements do not have an undesirable impact on other elements?
- Solution
- Identify points of predicted variation or instability
- Aassign responsibilities to create stable “interface” around them
- OCP and PV are two expressions of the same principle
- protection against change to the existing code and design at variation and evolution points with minor differences in emphasis
- Benefits
- Flexibility and Protection from Variation
- Provides more structured design
- Mechanisms motivated by PV
- Uniform access in C#, Ada, and Eiffel
- Service lookup
- Reflective or meta-model designs

Leave a comment